Cloud governance encompasses multifaceted principles and practices distinct from mere compliance. It is essential to clarify this distinction. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines cloud computing as a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider intervention.’
Governance, in turn, is defined as ‘the act or process of governing or overseeing the control and direction of something, such as a country or an organization.’ Therefore, we can distill the definition of cloud governance as the organizational oversight of the management, utilization, and direction of cloud services and resources provided by cloud service providers. This oversight extends to processes, systems, security, and cost management.
The term ‘cloud governance’ is sometimes used interchangeably with corporate policies, standards, and procedures about cloud computing operations, representing a subset of cloud governance.
To ensure effective cloud governance and the appropriate utilization of cloud resources, especially in regulated industries, adopting a ‘cloud-native’ mindset is imperative before delving into specific policies and procedures (PSPs) tailored for the cloud.
A well-structured cloud governance framework empowers organizations to leverage the benefits of cloud technology while proactively managing costs and mitigating operational and security risks. The significance of governance is magnified in the cloud environment, where the physical infrastructure constraints are eliminated, and agility and scalability reach new heights.
Traditional approaches to information technology infrastructure and compliance must be revised when applied to the cloud. Cloud governance must encompass processes that define and execute customized policies, standards, and procedures through automated systems, accommodating the speed and scale that cloud computing offers. This approach ensures protection, minimizes risks and maintains consistency.
Establishing effective cloud governance is a gradual process. It is best to start with a crawl-walk-run approach, tailoring the foundation and capabilities according to the organization’s specific needs. Striking a balance between business objectives, DevOps and cloud-native maturity, and operational priorities (such as reliability, security, feature deployment speed, and cost management) is crucial while upholding system confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
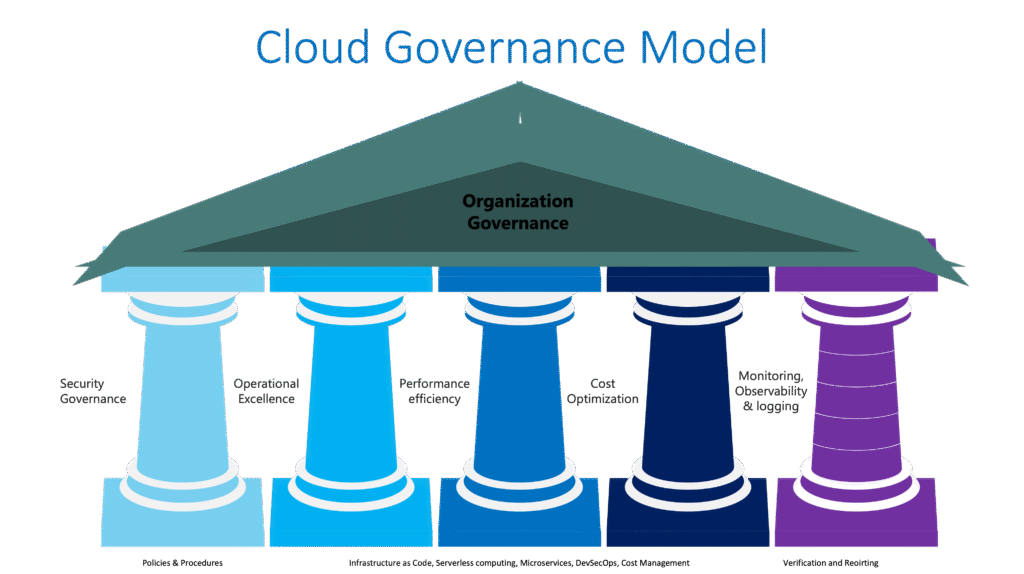
In the initial phase of cloud governance, three key areas should be addressed
Infrastructure as Code:
This practice facilitates version control of infrastructure and environments.
- Serverless Computing: Wherever feasible, consider running code without dedicated servers utilizing the REST API calls or batch processing. This approach optimizes costs, maximizes resource utilization, and fosters collaboration among developers, resulting in faster feature deployment.
- Monitoring and Telemetry: Comprehensive monitoring and telemetry tools provide real-time insights into cloud operations, enabling proactive decision-making.
Moving to Phase 2 of cloud governance involves doing the right things:
‘Doing the right thing’ precedes ‘doing things right’. The ease of provisioning cloud resources can lead to unintended consequences. Therefore, it is essential to adhere to well-architected principles for the cloud, focusing on five pillars of governance:
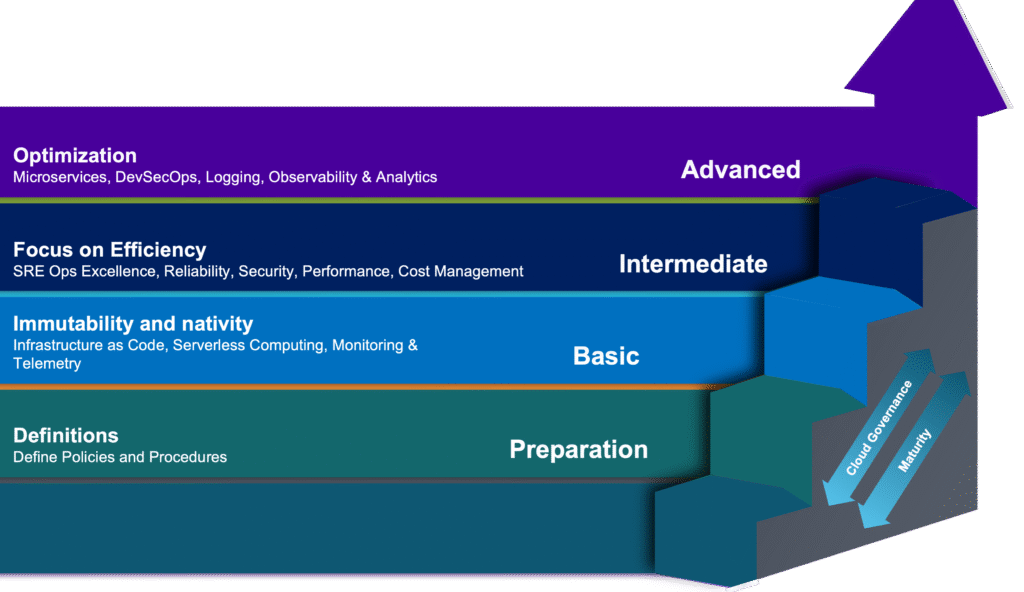
In Phase 3, Modernization becomes the primary focus:
- Microservices, Containers, and DevSecOps: Leveraging microservices, containers, and continuous integrations/continuous deployment pipelines (CI/CD) to enhance flexibility and agility. Securing your SDLC through threat modeling, static code testing, white box and black box testing, VAPT, and hackathons integrated with your DevOps eases complexities and saves runtime costs.
- Monitoring, Logging, Observability, and Analytics: Implement robust monitoring, observability, logging, and analytics solutions to gain insights into performance and security, providing relevant visualized dashboards, correlated drill-downs identifying the root cause, and providing impact information.
This comprehensive approach to cloud governance minimizes risks and optimizes organizational efficiency in the dynamic world of cloud computing.
